06. 练习:TensorFlow 里的线性函数
TensorFlow 里的线性函数
神经网络中最常见的运算,就是计算输入、权重和偏差的线性组合。回忆一下,我们可以把线性运算的输出写成:
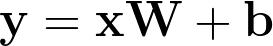
这里 \mathbf{W} 是连接两层的权重矩阵。输出 \mathbf{y},输入 \mathbf{x},偏差 \mathbf{b} 全部都是向量。
TensorFlow 里的权重和偏差
训练神经网络的目的是更新权重和偏差来更好地预测目标。为了使用权重和偏差,你需要一个能修改的 Tensor。这就排除了 tf.placeholder() 和 tf.constant(),因为它们的 Tensor 不能改变。这里就需要 tf.Variable 了。
tf.Variable()
x = tf.Variable(5)tf.Variable 类创建一个 tensor,其初始值可以被改变,就像普通的 Python 变量一样。该 tensor 把它的状态存在 session 里,所以你必须手动初始化它的状态。你将使用 tf.global_variables_initializer() 函数来初始化所有可变 tensor。
初始化
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)tf.global_variables_initializer() 会返回一个操作,它会从 graph 中初始化所有的 TensorFlow 变量。你可以通过 session 来调用这个操作来初始化所有上面的变量。用 tf.Variable 类可以让我们改变权重和偏差,但还是要选择一个初始值。
从正态分布中取随机数来初始化权重是个好习惯。随机化权重可以避免模型每次训练时候卡在同一个地方。在下节学习梯度下降的时候,你将了解更多相关内容。
类似地,从正态分布中选择权重可以避免任意一个权重与其他权重相比有压倒性的特性。你可以用 tf.truncated_normal() 函数从一个正态分布中生成随机数。
tf.truncated_normal()
n_features = 120
n_labels = 5
weights = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal((n_features, n_labels)))tf.truncated_normal() 返回一个 tensor,它的随机值取自一个正态分布,并且它们的取值会在这个正态分布平均值的两个标准差之内。
因为权重已经被随机化来帮助模型不被卡住,你不需要再把偏差随机化了。让我们简单地把偏差设为 0。
tf.zeros()
n_labels = 5
bias = tf.Variable(tf.zeros(n_labels))tf.zeros() 函数返回一个都是 0 的 tensor。
线性分类练习
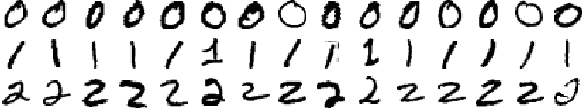
A subset of the MNIST dataset
你将试着使用 TensorFlow 来对 MNIST 数据集中的手写数字 0、1、2 进行分类。上图是你训练数据的小部分示例。你会注意到有些 1 在顶部有不同角度的 serif(衬线体)。这些相同点和不同点对构建模型的权重会有影响。

左: label 为 0 的权重。中: label 是 1 的权重。右: label 为 2 的权重。
上图是每个 label (0, 1, 2) 训练得到的权重。权重显示了它们找到的每个数字的特性。用 MNIST 来训练你的权重,完成这个练习。
说明
- 打开 quiz.py
- 实现
get_weights让它返回一个权重的tf.Variable - 实现
get_biases返回一个偏差的tf.Variable - 在
linear函数中实现xW + b
- 实现
- 打开 sandbox.py
- 初始化权重
因为 xW + b 中的 xW 是矩阵相乘,所以你要用 tf.matmul() 函数,而不是 tf.multiply()。不要忘记矩阵相乘的规则,tf.matmul(a,b) 不等于 tf.matmul(b,a)。
Start Quiz: